What is Auth0?¶
Quoted from https://auth0.com/docs/getting-started/overview
Auth0 provides authentication and authorization as a service. We are here to give developers and companies the building blocks they need to secure their applications without having to become security experts. You can connect any application (written in any language or on any stack) to Auth0 and define the identity providers you want to use (how you want your users to log in). Based on your app’s technology, choose one of our SDKs (or call our API), and hook it up to your app. Now each time a user tries to authenticate, Auth0 will verify their identity and send the required information back to your app.
Auth0 Central Components¶
ForwardAuth is built on the following central components from Auth0:
Authorization Code OAuth 2.0 grant-flow
Applications
APIs
Role Based Access Control
Users, Roles and Permissions
Rules
Applications¶
From the Auth0 documentation on Applications
Applications are primarily meant for human interaction, as opposed to APIs, which provide data to applications through a standardized messaging system.
The term application does not imply any particular implementation characteristics. For example, your application could be a native app that executes on a mobile device, a single-page app that executes on a browser, or a regular web app that executes on a server.
 The page for applications in Auth0
The page for applications in Auth0
API’s¶
The Auth0 documentation on APIs describes an API like this
An API is an entity that represents an external resource, capable of accepting and responding to protected resource requests made by applications. At the OAuth2 spec an API maps to the Resource Server.
When an application wants to access an API’s protected resources it must provide an Access Token. The same Access Token can be used to access the API’s resources without having to authenticate again, until it expires.
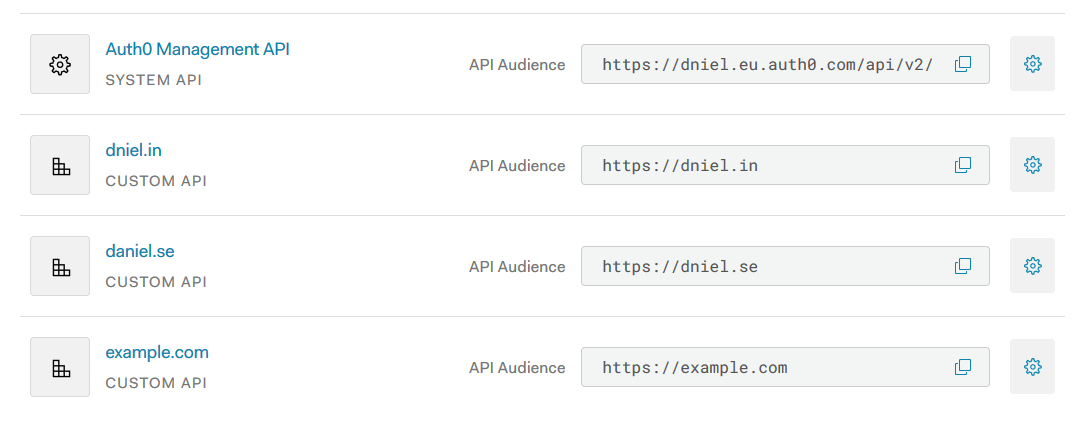 The page for APIs in Auth0
Register the web applications that you want to protect behind Traefik and ForwardAuth as APIs to be able to add
permissions to them. You can also represent Multiple APIs Using a Single Logical API in Auth0
so that they doesn’t need to re-authenticate when navigating between services.
The page for APIs in Auth0
Register the web applications that you want to protect behind Traefik and ForwardAuth as APIs to be able to add
permissions to them. You can also represent Multiple APIs Using a Single Logical API in Auth0
so that they doesn’t need to re-authenticate when navigating between services.
Enable RBAC for the API on the same page¶
The new system for Auth0 RBAC is being released gradually during 2019 to replace the current Authorization Extension.
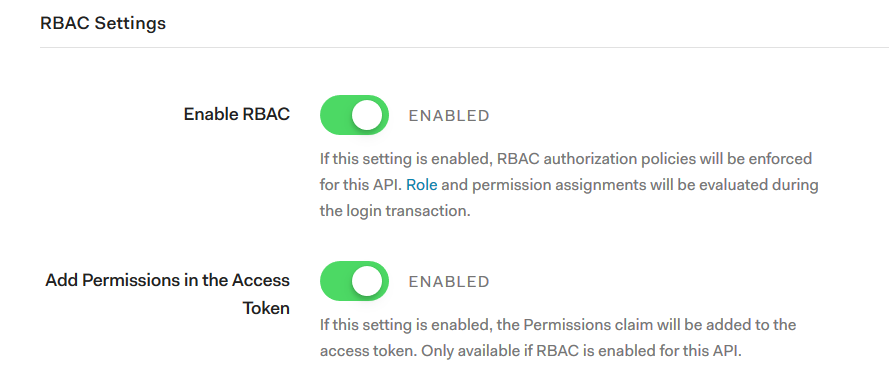 The section for RBAC settings in Auth0
To use Auth0 RBAC for your API you need to go to the settings of your API.
The section for RBAC settings in Auth0
To use Auth0 RBAC for your API you need to go to the settings of your API.
Click on the enable switch, and also the “Add Permissions to Access Token” so that ForwardAuth can see them in the returned token.
Under Permissions in your API’s settings create permissions for your API.
Go to Users & Roles and add either directly to a user the permissions you created in your API, or create a role with a set of permissions and assign to your users.
The RBAC system will run when the user log in and match all the scopes you send in to the permissions of the user. Any permissions requested by the user that they dont have, will be removed by the RBAC system when returning the response.
If you dont enable RBAC for your API, or dont enable “Add permissions to Access Token” everybody will be let through to the API.
Create and add permissions to the API¶
Add permissions to your API.
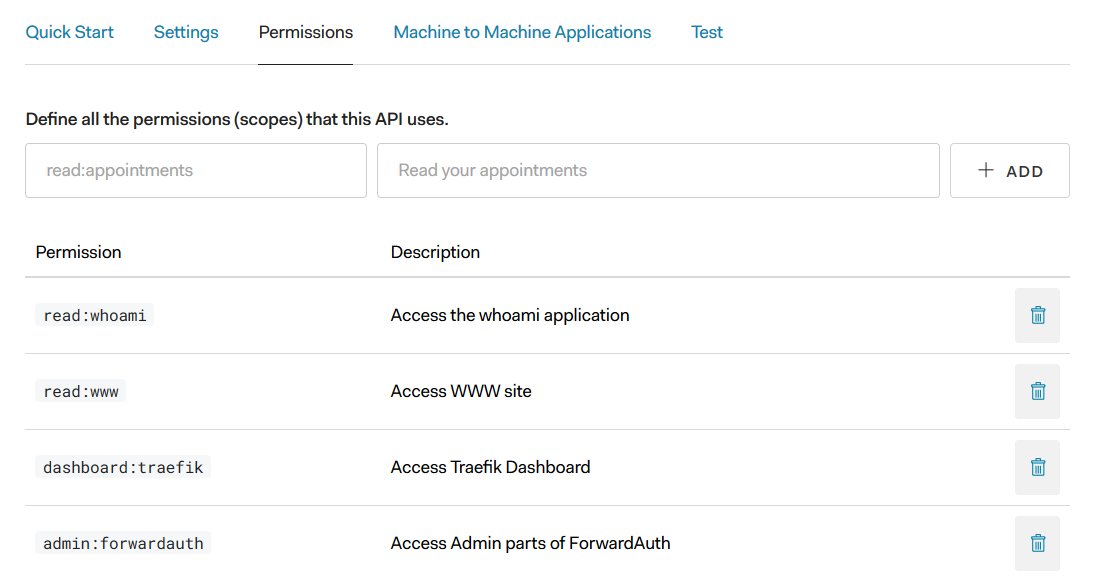 The page for API Settings in Auth0
The page for API Settings in Auth0
Users and Roles¶
Roles is a collection of permissions that are assignable to Users.
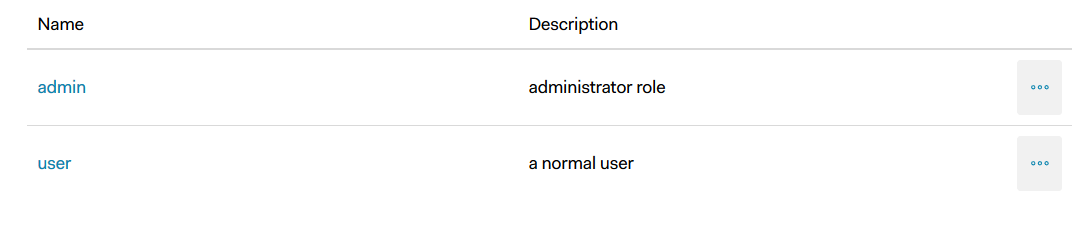 The section for RBAC settings in Auth0
The section for RBAC settings in Auth0
Assign permissions to the Roles.¶
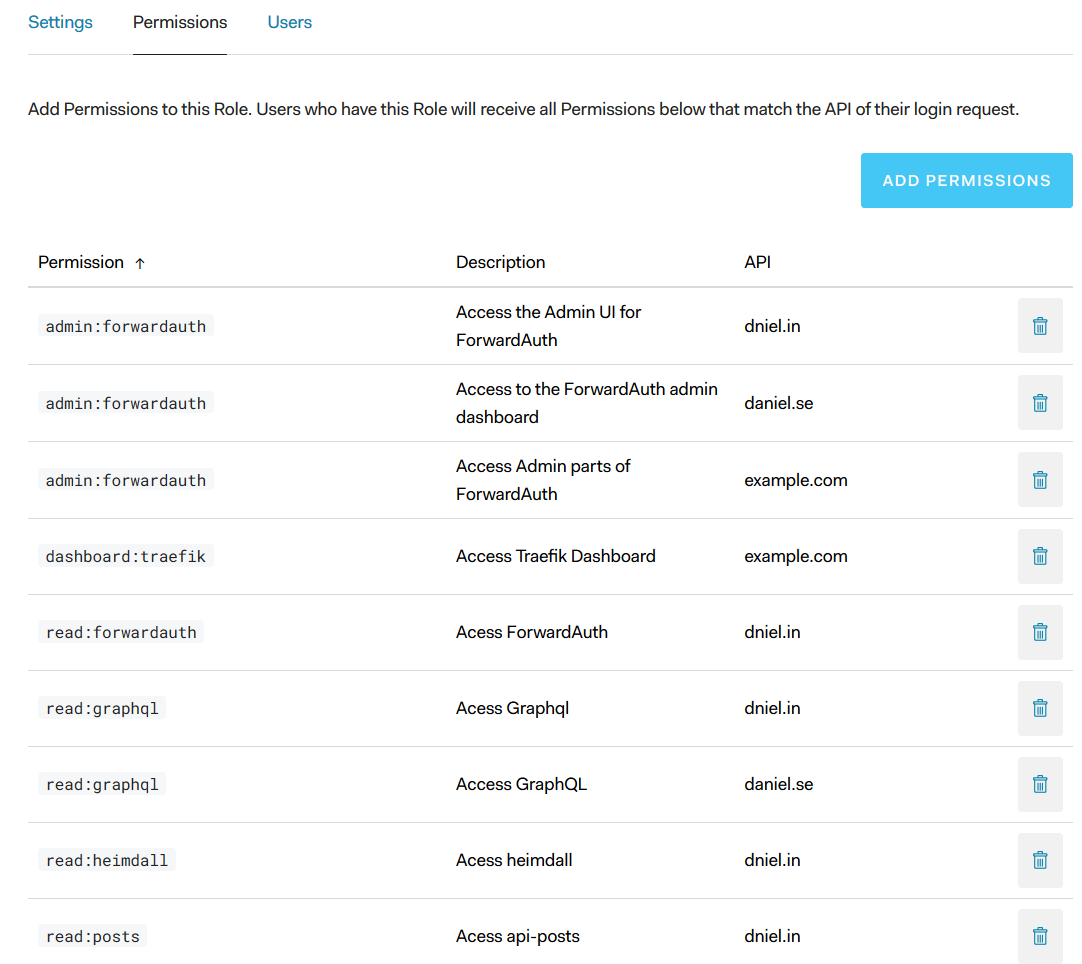 The section for RBAC settings in Auth0
The section for RBAC settings in Auth0
Require Permissions to access an application in ForwardAuth¶
In the application.yaml file for ForwardAuth add a required-permissions to assign permissions that ForwardAuth
will check before letting the user access the application. The permissions is transferred on login from Auth0
to ForwardAuth using the Access Token when the Access Token is a JWT Token, i.e, the audience for an API has been
set. This also means that permissions is only useful for access control to API’s. There is no way to assign permissions
to applications in Auth0.
The required-permissions is an Array of permissions and if the user that tries to login and access an application does not have the required permissions an HTTP 403 Forbidden will be thrown and an error page will be displayed. E.g,
apps:
- name: whoami.example.test
audience: https://whoami.dniel.se
required-permissions:
- write:whoami
- read:whoami
Rules¶
Quoted from Auth0 page about rules
Rules are JavaScript functions that execute when a user authenticates to your application. They run once the authentication process is complete, and you can use them to customize and extend Auth0’s capabilities. For security reasons, your Rules code executes isolated from the code of other Auth0 tenants in a sandbox.
See the page receipts for examples and inspiration of custom rules that I have written.
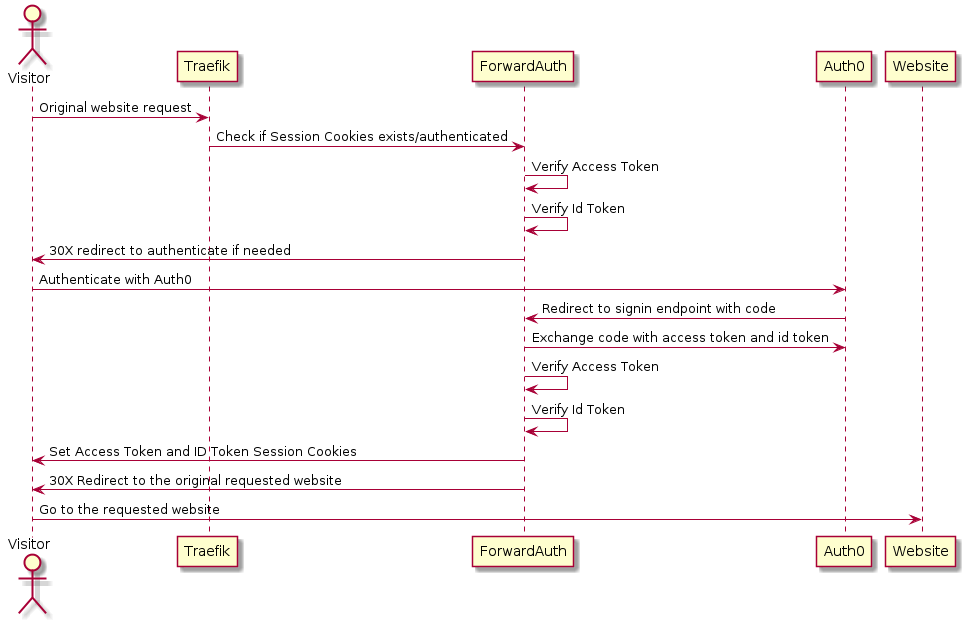 the authentication and authorization prosess
the authentication and authorization prosess